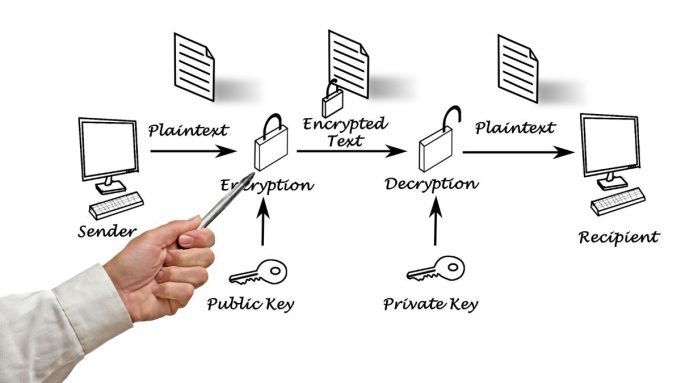
The introduction of public-key cryptography (PKC) revolutionised the world of cryptography. Unlike symmetric cryptography that uses a single key, public-key cryptography employs two different keys: a public key and a private key. This form of cryptography has become essential for modern computer security and the growing cryptocurrency industry. But what is public-key cryptography and how does it work?
A public-key cryptography system consists of two key pairs: a public key and a private key. The public key is used by a sender to encrypt data while the private key is used by the recipient to decrypt the data. Essentially, the public key is publically available while the private must be kept secure. This means that if anyone were to obtain the private key, they would be able to decrypt any messages sent using the corresponding public key. Because private keys must be kept secure, public-key algorithms usually use longer, more complex key lengths. One of the most widely used algorithms is known as RSA, which uses a modulus created by multiplying two prime numbers to generate unique key pairs.
Public-key cryptography is frequently used as an encryption tool. It helps to solve one of the long-standing issues of symmetric cryptography by allowing for the secure transfer of the encryption key. Without the need for keys to be manually shared or exchanged, digital messages can be securely encrypted and sent through even an insecure connection. Furthermore, encryption algorithms are also used for digital signatures. These signatures use the sender’s public key to check the integrity of a message. In some cases, both encryption and signatures are applied to a message.
Despite its advantages, public-key cryptography does have its limitations. Most notably, it is relatively slow compared to symmetric algorithms. Additionally, public-key cryptography relies on the assumption that private keys are kept in secret. If a private key were to be exposed, the security of any messages encrypted with its corresponding public key would be compromised.
Public-key cryptography is in use in a variety of applications. It is used to encrypt emails and messages, ensure secure connections to websites through the secure sockets layer (SSL) protocol, and is even being explored as an method of electronic voting. Of course, public-key cryptography also plays a major role in the blockchain and cryptocurrency sphere. Every cryptocurrency wallet is tied to a key pair, with the public key used for the wallet address and the private key used for creating digital signatures. It is the use of digital signatures that allows for the secure verification of cryptocurrency transactions, hence their importance in the industry.
In conclusion, public-key cryptography is an essential component of modern computer security and the cryptocurrency ecosystem. It is used to securely transfer encryption keys and as a verification tool for digital signatures. This form of asymmetric cryptography offers a greater level of security than symmetric algorithms and has enabled the creation of many new applications and uses.